Summary
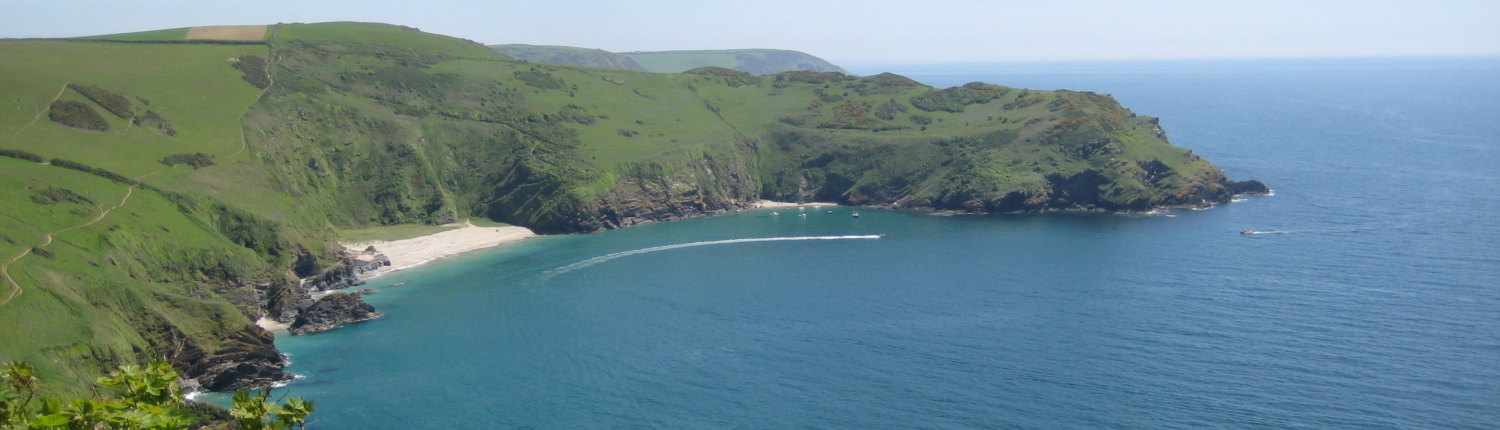
The study sought to explore ecosystem services assessments at the marine planning scale incorporating a combination of data rich and data poor areas, and to generate information that could help inform delivery of the Cornwall Maritime Strategy. As many ecosystem services as possible were to be considered, with a separate focus on cultural services.
For additional information
Date: 2012-2015
The work presented here has been developed in six case studies of the VALMER Interreg 4A Channel project (2012-2015).
Coordination by M. Philippe, J. Ballé-Béganton and D. Bailly1
based on written contributions from N. Smith, P. Hoskin, W. Dodds, T. Hooper, L. Friedrich, N. Beaumont and C. Grifths